Introduction
This article outlines instructions on how to disable IPv6 on your Webdock server.
This might come handy if you want to disable IPv6, maybe temporarily, to force your server (and the services running) to use IPv4, or for some other reasons.
Prerequisites
- An already provisioned Webdock server
- A sudo shell user
- SSH access to your server.
Temporarily Disabling IPv6
Using sysctl IPv6 can be disabled. However, these changes are not permanent. So after you reboot your server, IPv6 will start working again. If you want IPv6 disabled permanently, skip to the next relevant section.
Execute the below commands to disable IPv6 temporarily.
$ sudo sysctl -w net.ipv6.conf.all.disable_ipv6=1 $ sudo sysctl -w net.ipv6.conf.default.disable_ipv6=1 $ sudo sysctl -w net.ipv6.conf.lo.disable_ipv6=1
Now, IPv6 will be disabled and pinging an IPv6 address will not work, for example.
Permanently Disabling IPv6
For Ubuntu/Debian servers:
To disable IPv6, run
For Ubuntu:
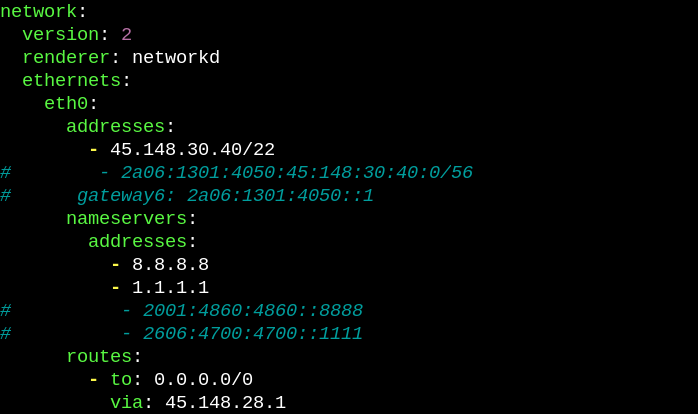
$ sudo nano /etc/netplan/50-cloud-init.yaml
Comment the IPv6 lines with “#” so that it looks something like this:
For Debian:
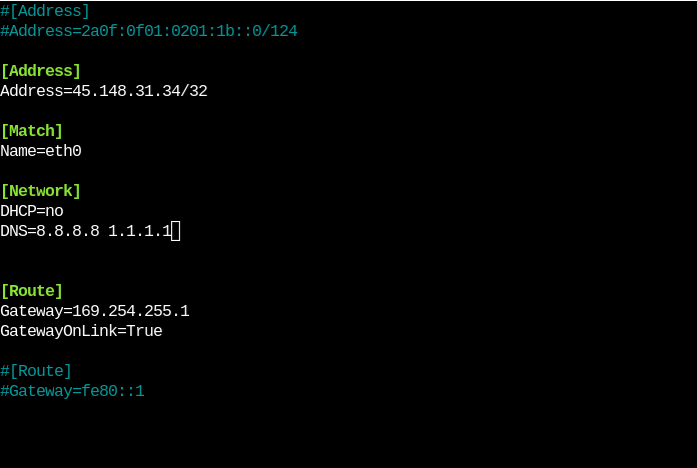
$ sudo nano /etc/systemd/network/10-cloud-init-eth0.network
Comment the IPv6 lines with “#” so that it looks something like this:
Reboot the server now for the changes to take affect.
If you want to re-enable IPv6, just undo the changes (remove the “#”s) and reboot your server.
For AlmaLinux/CentOS servers:
On AlmaLinux and CentOS servers, we use NetworkManager to configure network. To disable IPv6, run
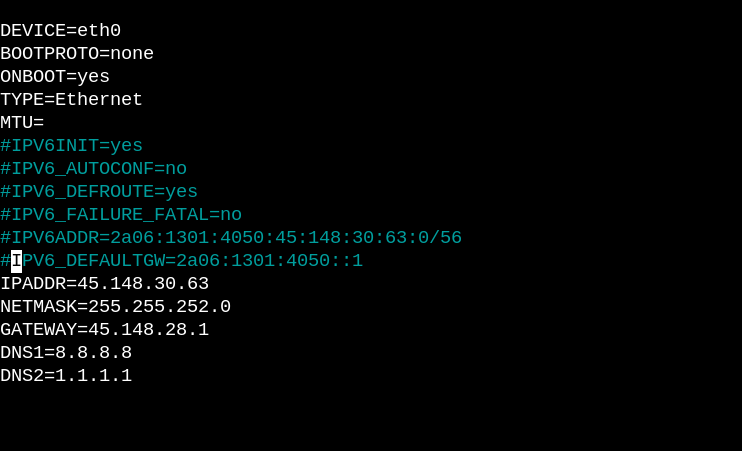
$ sudo nano /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eth0
Comment the IPv6 lines with “#” so that it looks something like this:
Reboot the server now for the changes to take affect.
If you want to re-enable IPv6, just undo the changes (remove the “#”s) and reboot your server
Conclusion
This article outlined steps to disable IPv6 on your Webdock server either temporarily or permanently.
Contact Webdock Support if you run into any errors or need further assistance.